Allergies affect millions of people worldwide, causing symptoms ranging from mild irritation to severe, life-threatening reactions. If you suspect you have allergies but aren’t sure what triggers your symptoms, allergy testing can provide clarity. Understanding your specific allergens is the first step toward effective management and improved quality of life.
What Is Allergy Testing?
Allergy testing is a medical procedure used to identify substances (allergens) that cause allergic reactions in an individual. Allergens can include:
- Pollen
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
- Mold spores
- Foods like nuts, eggs, or shellfish
- Insect stings
- Certain medications
By pinpointing the exact allergens causing your symptoms, healthcare providers can recommend tailored treatments or avoidance strategies.
Common Symptoms That Indicate the Need for Allergy Testing
You might consider allergy testing if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Sneezing, runny or stuffy nose (allergic rhinitis)
- Itchy, watery eyes
- Skin reactions such as hives, eczema, or rash
- Asthma symptoms like wheezing or shortness of breath triggered by specific exposures
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat after eating certain foods
- Frequent sinus infections or ear infections
- Severe reactions to insect stings or medications
If these symptoms interfere with your daily life or don’t respond well to over-the-counter treatments, allergy testing can be an important diagnostic step.
Types of Allergy Testing
There are several methods used to detect allergies, and the choice depends on your symptoms, age, and medical history.
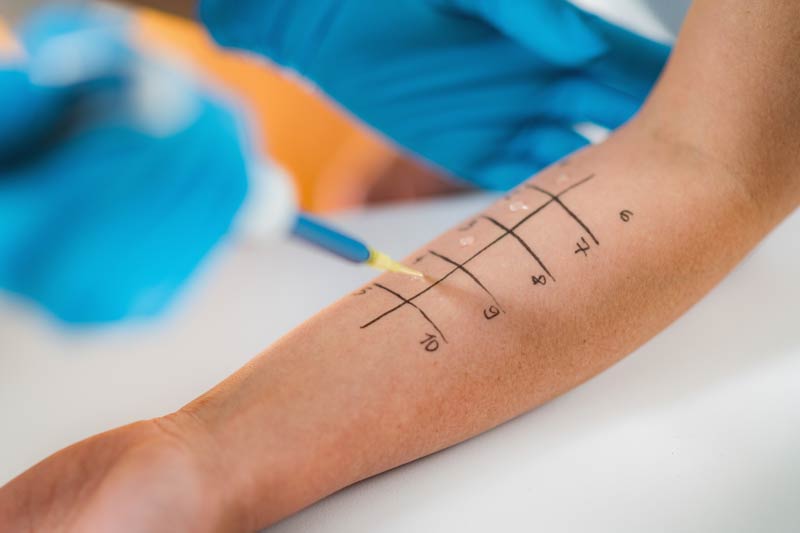
1. Skin Prick Test (SPT)
The most common and widely used allergy test, the skin prick test involves placing tiny drops of suspected allergens on the skin—usually the forearm or back. The skin is then gently pricked or scratched through the drops to allow allergens to enter the skin’s surface.
If you are allergic to a substance, you will develop a small raised bump (similar to a mosquito bite) within 15-20 minutes at the test site. The size of the bump helps determine the severity of the reaction.
Advantages:
- Quick results (within 20 minutes)
- Safe and generally painless
- Can test multiple allergens at once
Limitations:
- Not suitable for people with certain skin conditions or who are on medications that affect test accuracy
- Risk of mild localized reactions
2. Blood Test (Specific IgE Test)
Also known as the RAST test or ImmunoCAP test, this blood test measures the amount of allergen-specific antibodies (IgE) in your blood.
Advantages:
- Useful if skin tests aren’t possible (e.g., severe eczema, pregnancy, or medication use)
- Can test for many allergens simultaneously
- No risk of skin reactions
Limitations:
- Results take longer (a few days)
- May be less sensitive than skin prick tests
3. Patch Test
Used primarily to diagnose contact dermatitis, patch testing involves placing adhesive patches containing allergens on your back for 48 hours. The skin is then examined for reactions over several days.
Advantages:
- Identifies delayed allergic reactions to substances like metals, fragrances, or chemicals
Limitations:
- Longer testing period
- Requires multiple visits to the doctor
Preparing for Allergy Testing
To get accurate results, certain preparations are necessary:
- Avoid antihistamines and certain other medications for several days before testing (your doctor will provide specific instructions).
- Inform your provider about any medications, medical conditions, or pregnancy.
- Wear comfortable clothing that allows easy access to your arms or back.
- Avoid applying lotions or creams on the test area before skin tests.
What to Expect During and After the Test
For skin prick testing, the procedure usually takes less than 30 minutes. You may experience mild itching or redness at test sites. After the test, your healthcare provider will explain the results and discuss the next steps.
Blood tests require a simple blood draw and usually have no side effects.
Patch tests require wearing patches for 48 hours, and you’ll need to avoid getting them wet.
How Allergy Testing Helps in Managing Allergies
Identifying your allergens allows your healthcare provider to recommend personalized treatment plans, which may include:
- Avoidance strategies to reduce exposure
- Medications such as antihistamines, nasal sprays, or inhalers
- Allergy immunotherapy (allergy shots or tablets) to gradually desensitize your immune system
- Emergency action plans for severe allergies
With accurate allergy identification, you can significantly reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life.
When Should You Get Allergy Testing?
You should consider allergy testing if:
- You experience persistent or severe allergy symptoms.
- Over-the-counter treatments are ineffective.
- Your symptoms worsen during certain seasons or after exposure to specific environments.
- You have a family history of allergies or asthma.
- You experience unexplained skin rashes or reactions.
- You suspect food allergies, especially after adverse reactions to certain foods.
Conclusion
Allergy testing is a valuable tool to uncover hidden allergens that may be impacting your health. By accurately diagnosing allergies, you empower yourself and your healthcare provider to develop effective management strategies, prevent complications, and improve your overall quality of life.